Delay Time Selects the Concentration
The time interval elapsing between the moment of injection ( I ) and of detection is the Delay Time. Delay time determines which section ( ) of the sample zone will be arrested in the observation field of a detector ( ) for the reaction rate measurement. Since the analyte (red) disperses within the reagent stream (blue) on the way to the detector while the product (yellow) is being formed, it is essential that the delay time is perfectly reproduced for each assay. In the example shown, longer delay times will yield lower slopes, since tail sections of the sample zone are more diluted; and shorter delay times (up to the peak maximum) will yield steeper slopes. In the absence of analyte, a horizontal (blank) line will be observed.
1.2.24.
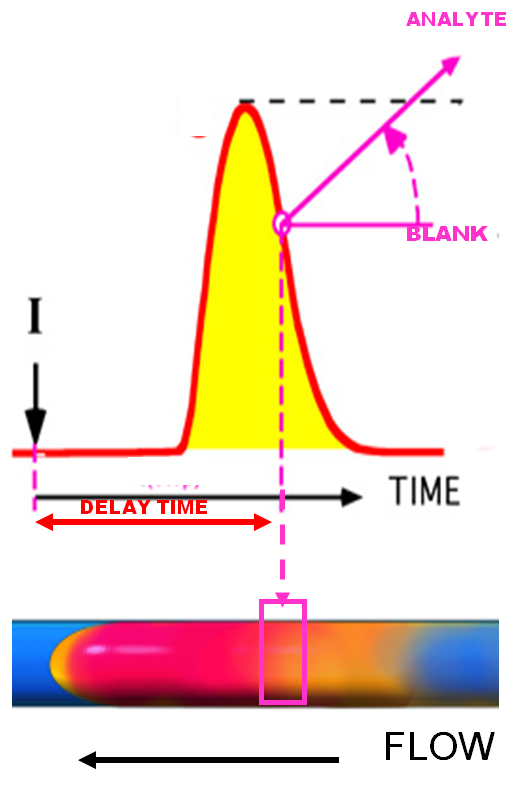
Note: Delay time, while easier to describe and understand, can be applied only when a forward flow is used. For SI, which uses flow reversal a return volume has to be used, for programming the assay protocol (Chapter 1).